What is an SSL certificate?
August 28, 2018
Digital certificates serve as the backbone of internet security.
An SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates the identity of a website and encrypts information sent to the server using SSL technology. Encryption is the process of scrambling data into an undecipherable format that can only be returned to a readable format with the proper decryption key. When you use an SSL certificate, an encrypted connection is established between a browser or user‘s computer and a server or website. The SSL connection protects sensitive data, such as credit card information, exchanged during each visit, which is called a session, from being intercepted from non-authorized parties.
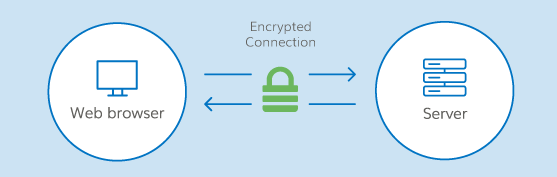

A certificate serves as an electronic "passport" that establishes an online entity‘s credentials when doing business on the Web. When an Internet user attempts to send confidential information to a Web server, the user‘s browser accesses the server‘s digital certificate and establishes a secure connection.
An SSL certificate contains the following information:
-- The certificate holder‘s name
-- The certificate‘s serial number and expiration date
-- A copy of the certificate holder‘s public key
-- The digital signature of the certificate-issuing authority
